The asset safety allowance shelters a portion of dad or mum property on the Free Utility For Federal Pupil Support (FAFSA). This helps extra college students qualify for needs-based monetary support.
Sadly, the FAFSA asset safety allowance has been steadily reducing for over a decade. And on the 2023-2024 FAFSA (which households will begin submitting on October 1, 2022) it’ll drop to zero for all mother and father.
Why are these adjustments occurring and the way will college students be impacted financially? We’ll reply each of these questions beneath. We’ll additionally make just a few suggestions for the way Congress can tackle the asset safety allowance drawback.
What Is The FAFSA Asset Safety Allowance?
The FAFSA collects details about the earnings and property of pupil and oldsters, family dimension, and variety of youngsters in faculty, amongst different elements. This data is used to calculate the Anticipated Household Contribution (EFC), a measure of a household’s monetary energy.
The FAFSA subtracts the asset safety allowance, which is predicated on the age of the older dad or mum, from dad or mum property earlier than assessing a portion of what’s left. The aim of the asset safety allowance is to shelter sufficient financial savings to cowl the distinction between common Social Safety retirement advantages and a average household earnings stage.
The asset safety allowance was additionally supposed to shelter a portion of faculty financial savings. However this was by no means applied by Congress, although the Greater Training Act of 1965 refers to an “Training Financial savings and Asset Safety Allowance.”
How Is The Asset Safety Allowance Altering?
For greater than a decade, the common Social Safety retirement profit has elevated whereas the average household earnings stage has remained roughly the identical. This has precipitated the asset safety allowance to lower considerably after reaching a peak in 2009-2010.
This Federal Register discover exhibits that the asset safety allowance will drop to zero for single mother and father of all ages for the 2022-23 FAFSA. That is down from $3,900 for age 65 and older final yr and $32,800 in 2009-2010. For single mother and father age 48, the median age of oldsters of college-age youngsters, the asset safety allowance is down from $2,500 final yr and $21,400 in 2009-2010.
The asset safety allowance for married mother and father will drop to $5,900 for fogeys age 65 and older. That is down from $10,500 final yr (a 44% drop) and $84,000 in 2009-2010 (a 93% drop). For married mother and father age 48, the asset safety allowance will drop to $3,700. It was $6,000 final yr and $52,400 in 2009-2010.
For the 2023-2024 FAFSA (which college students will start submitting in October 2022), the asset safety allowance for fogeys will probably be $0.
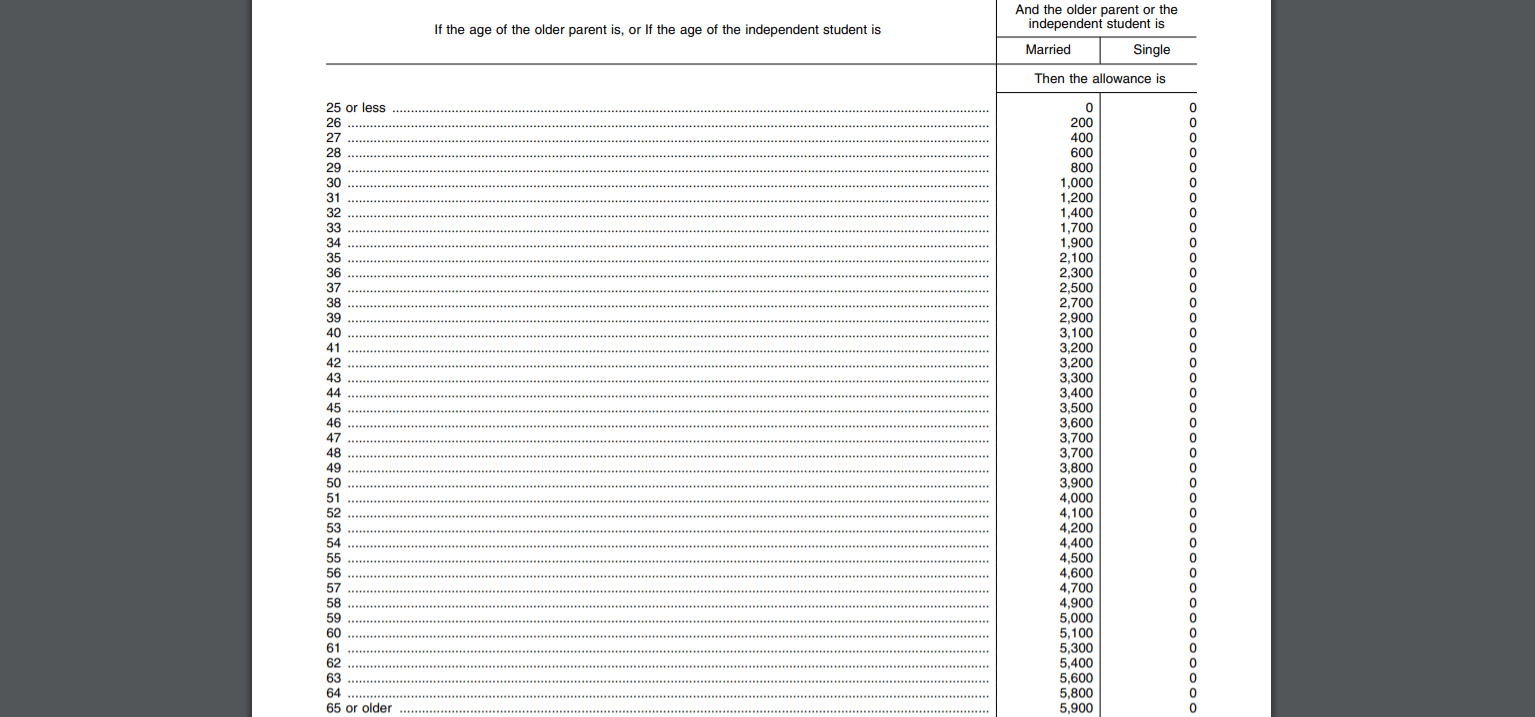
Which means that the property of oldsters won’t be sheltered when calculating the anticipated household contribution (EFC). And that reduces eligibility for need-based monetary support.
What Will Be The Monetary Influence Of The Modifications?
The lower within the asset safety allowance from $84,000 to $5,900 is the equal of a $4,400 change within the EFC. Which means that households are getting as a lot as $4,400 much less in need-based monetary support than they in any other case would have acquired.
Many households aren’t conscious that the asset safety allowance is inflicting a giant drop in eligibility for grants, scholarships, and backed pupil loans. The monetary support formulation perform like a black field. And the influence of the adjustments can also be partially masked by inflationary changes to different points of the monetary support method.
The web result’s that the EFC has remained flat or elevated whilst capacity to pay for faculty has decreased. This very true amongst middle-income households who aren’t eligible for the simplified wants check. The simplified wants check causes property to be ignored for households that earn lower than $50,000 per yr or who’re eligible for sure means-tested federal advantages.
How To Repair The Asset Safety Allowance Downside
Solely Congress can repair the asset safety allowance drawback. Sadly, this drawback was not tackle by the FAFSA simplification laws that was included within the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2021.
One attainable answer is to exclude faculty financial savings plans (akin to 529 plans, pay as you go tuition plans and Coverdell Training Financial savings Accounts) from reportable property and certified distributions from earnings on the FAFSA. Non-qualified distributions ought to proceed to be included in adjusted gross earnings on the FAFSA.
This answer wouldn’t solely tackle the issue but in addition remove any precise or perceived penalty for saving for faculty. Alternately, one might exclude all property from the FAFSA (not simply faculty financial savings plans). This could additional simplify the FAFSA.
A 3rd answer can be to shelter a set greenback quantity (akin to $50,000 per little one) and alter the quantity yearly for inflation. That may be sufficient to shelter faculty financial savings for nearly two years of faculty prices at an in-state 4-year public faculty and one yr of faculty prices at a 4-year personal faculty.

