The temporary’s key findings are:
- The worth of Social Safety’s retirement program to people is commonly measured by evaluating anticipated advantages to payroll taxes.
- However this method ignores this system’s insurance coverage worth, which is bigger for these with extra unsure lifespans.
- The evaluation estimates the insurance coverage worth utilizing a lifecycle mannequin for stylized households by race, schooling, and marital standing.
- Accounting for insurance coverage worth, the outcomes present that this system is considerably extra invaluable than lifetime taxes for nearly all family varieties.
- Social Safety’s insurance coverage element additionally will increase racial fairness, as a result of lifespans range extra amongst Black people.
Introduction
Social Safety helps Black people and people with low academic attainment – and due to this fact low earnings – by way of its progressive profit construction. However, the character of Previous-Age and Survivors Insurance coverage (OASI) as a life annuity inherently will increase anticipated lifetime advantages for people who are likely to dwell longer. No matter how these elements stability out, although, wanting solely at anticipated advantages doesn’t present a full image of Social Safety’s worth. Particularly, it neglects this system’s longevity insurance coverage worth, which favors Black beneficiaries and people with much less schooling as a result of they sometimes face higher uncertainty over how lengthy they are going to dwell.
This temporary, based mostly on a latest paper, assesses the worth of OASI, together with this system’s longevity insurance coverage worth, by race, gender, marital standing, and schooling; and it estimates the extent to which incorporating longevity insurance coverage enhances the equalizing impact of OASI.
The dialogue proceeds as follows. The primary part explains why OASI’s worth may differ by race and socioeconomic standing (SES). The second part describes the information and methodology. The third part presents the outcomes. The ultimate part concludes that after the insurance coverage worth of OASI is taken into account, this system is considerably extra invaluable than the lifetime OASI payroll taxes paid for nearly all family varieties; and OASI will increase racial fairness in retirement safety greater than is usually recommended by measures of anticipated advantages alone.
Background
OASI advantages are generally evaluated by way of cash’s value: the current worth of anticipated advantages relative to contributions. The progressive profit formulation supplies higher charges of return on contributions for teams with decrease lifetime earnings, whereas the longer life expectations of upper earners imply that they are going to obtain advantages for an extended time period.
The cash’s value method, nonetheless, neglects the longevity insurance coverage offered by this system. OASI is a life annuity, so it provides households safety in opposition to outliving their sources, and the worth of this safety will increase with the unpredictability of their lifespan. It seems that OASI longevity insurance coverage is especially necessary for Black households and people with low schooling, as a result of, whereas these teams have decrease common lifespans than others, they face higher uncertainty round their averages. The next evaluation makes use of a structural mannequin to look at each OASI’s insurance coverage worth and its cash’s value by race and SES.
Knowledge and Methodology
The evaluation considers stylized households, differentiated by race (Black or White), SES (low- or high-education), and family composition (single man, single lady, or married couple). This course of leads to 12 stylized households (8 singles by gender, schooling, and race; and 4 {couples} by schooling and race) that differ by way of their mortality possibilities, lifetime earnings, pension earnings, Social Safety advantages, and wealth at age 65.
The info used to assemble the stylized households’ OASI advantages, payroll tax contributions, and monetary traits are from the Well being and Retirement Research linked to administrative earnings data. The calculation of mortality charges by race and SES is predicated on mortality knowledge from the Nationwide Important Statistics System and demographic and SES info from the American Group Survey. Desk 1 exhibits that Black households at age 65 usually have a shorter life expectancy than White ones, whereas in addition they face higher variance round their common lifespans.
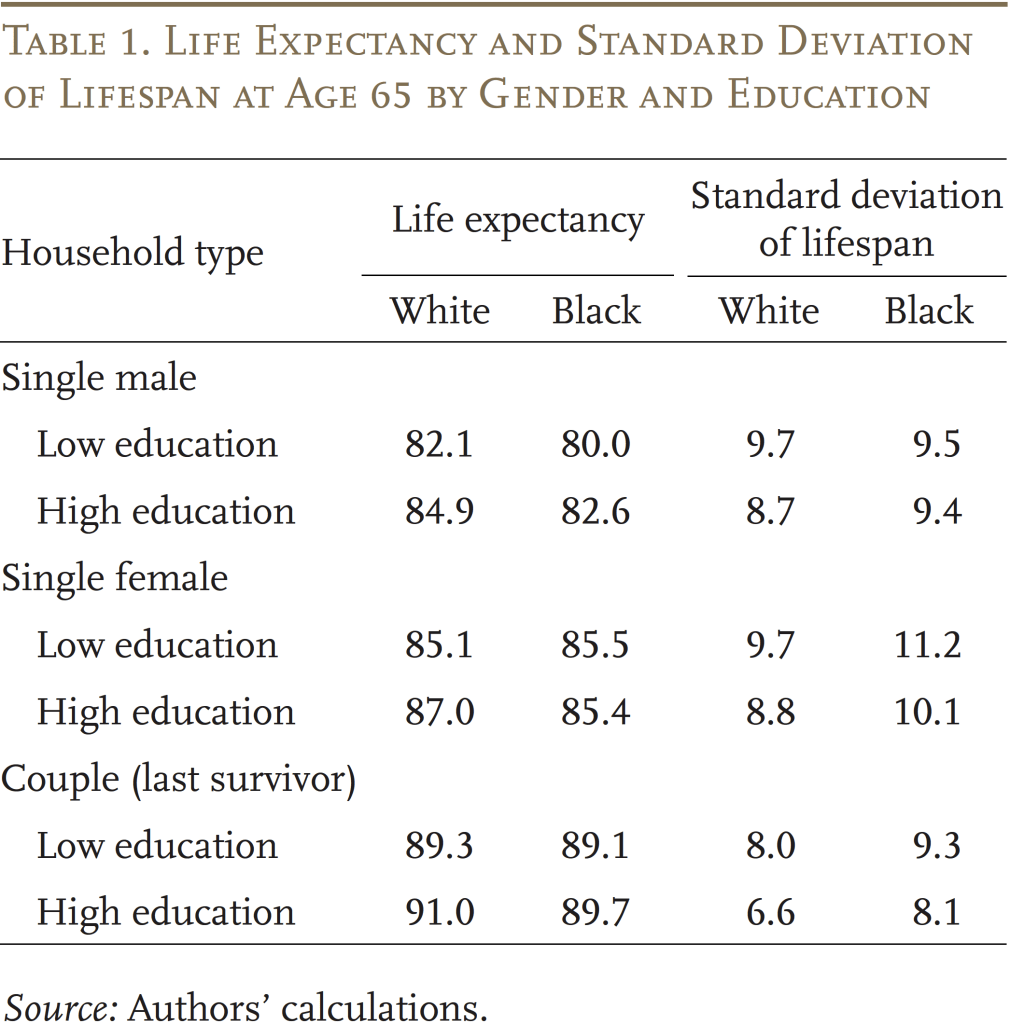
The calculation of the cash’s value of OASI is easy: the anticipated current worth of every family’s advantages is expounded to the lifetime contributions of the family to the OASI program. On this calculation, future advantages are discounted at a 2-percent charge and by the anticipated mortality possibilities for every family’s demographic traits. This calculation leads to a measure of the anticipated return on every greenback of contributions from a purely monetary perspective, neglecting any insurance coverage worth.
Subsequent, to measure Social Safety’s longevity insurance coverage, the evaluation estimates OASI’s “wealth equivalence.” This measure displays how rather more wealth households would must be as properly off in a world with no OASI program as they’re with this system. As a result of households pay into this system throughout their working years, this wealth equivalence can also be associated to lifetime contributions, yielding a ratio of wealth-to-contributions (W-to-C). This ratio signifies how a lot worth, measured in {dollars}, households derive from each greenback they contribute to OASI.
Calculating wealth equivalence requires a lifecycle mannequin. Within the mannequin, households select their consumption optimally to maximise their anticipated lifetime utility, contemplating their obtainable sources and their survival uncertainty. The wealth equivalence of OASI for every stylized family is estimated in two steps. First, the anticipated lifetime utility at age 65 for the family is calculated with OASI advantages; second, the calculation is repeated in a world with out OASI advantages to seek out the quantity of extra wealth at age 65 the family would must be simply compensated for not having the OASI profit.
Each the W-to-C ratio and the cash’s value calculation measure the lifetime worth of OASI advantages relative to the corresponding tax funds. Nevertheless, solely the previous accounts for the longevity insurance coverage worth of OASI and is, due to this fact, anticipated to be higher than the latter. Thus, evaluating these two measures sheds mild on the extent to which neglecting longevity insurance coverage underestimates the worth of OASI to numerous forms of households.
Outcomes
Desk 2 exhibits the cash’s value and the W-to-C ratio of OASI for the stylized households. Because the OASI program is meant to be actuarially balanced for the overall inhabitants, the cash’s value ratios for the stylized households range round 1. Cash’s value additionally tends to be larger for girls than males, reflecting each their decrease earnings (which will increase the return on contributions as a result of progressivity of advantages) and their longer life expectancy, which suggests they are going to obtain advantages for extra years. In distinction, the patterns by race and schooling are extra blended: on the one hand, Black and lower-education households profit from progressivity because of their decrease earnings. However, these households even have decrease life expectations, offsetting the progressivity to some extent.
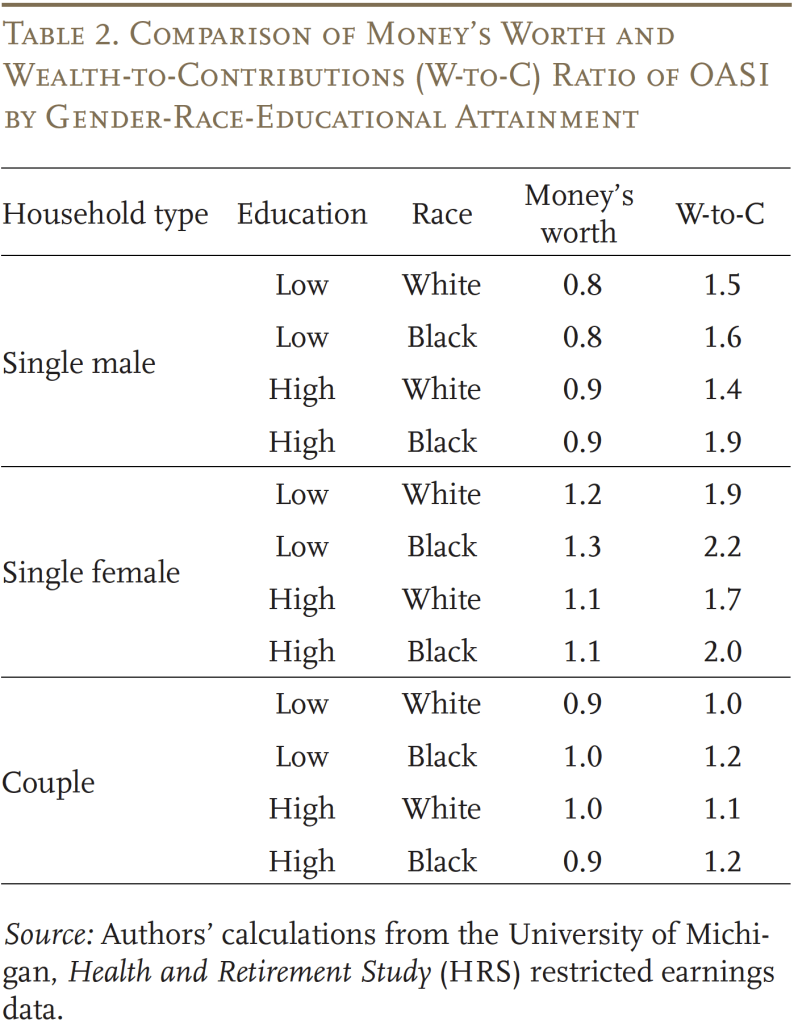
In distinction to cash’s value, the W-to-C ratio is strictly bigger than 1 for nearly all households. The truth that W-to-C is bigger than 1 implies that the majority households, no matter race, gender, schooling, or family composition, want a world by which OASI exists to at least one by which it doesn’t. Furthermore, on the margin, virtually all households must be keen to pay slightly extra into the system if essential to protect its profit ranges. Moreover, as anticipated, the W-to-C ratios are higher than cash’s value for all family varieties, implying households worth longevity insurance coverage.
The distinction between the W-to-C ratio and the cash’s value ratio serves as an approximate measure of the longevity insurance coverage worth of OASI. This worth is particularly giant for singles (for all singles mixed, it’s value about 80 % of complete payroll tax paid on common; see Determine 1). In distinction, {couples} have significantly decrease W-to-C ratios which suggest average longevity insurance coverage values (value 10 to twenty % of complete payroll tax paid). This outcome displays the truth that a considerable portion of the longevity danger might be self-insured between relations who allow different relations to obtain their wealth after loss of life.
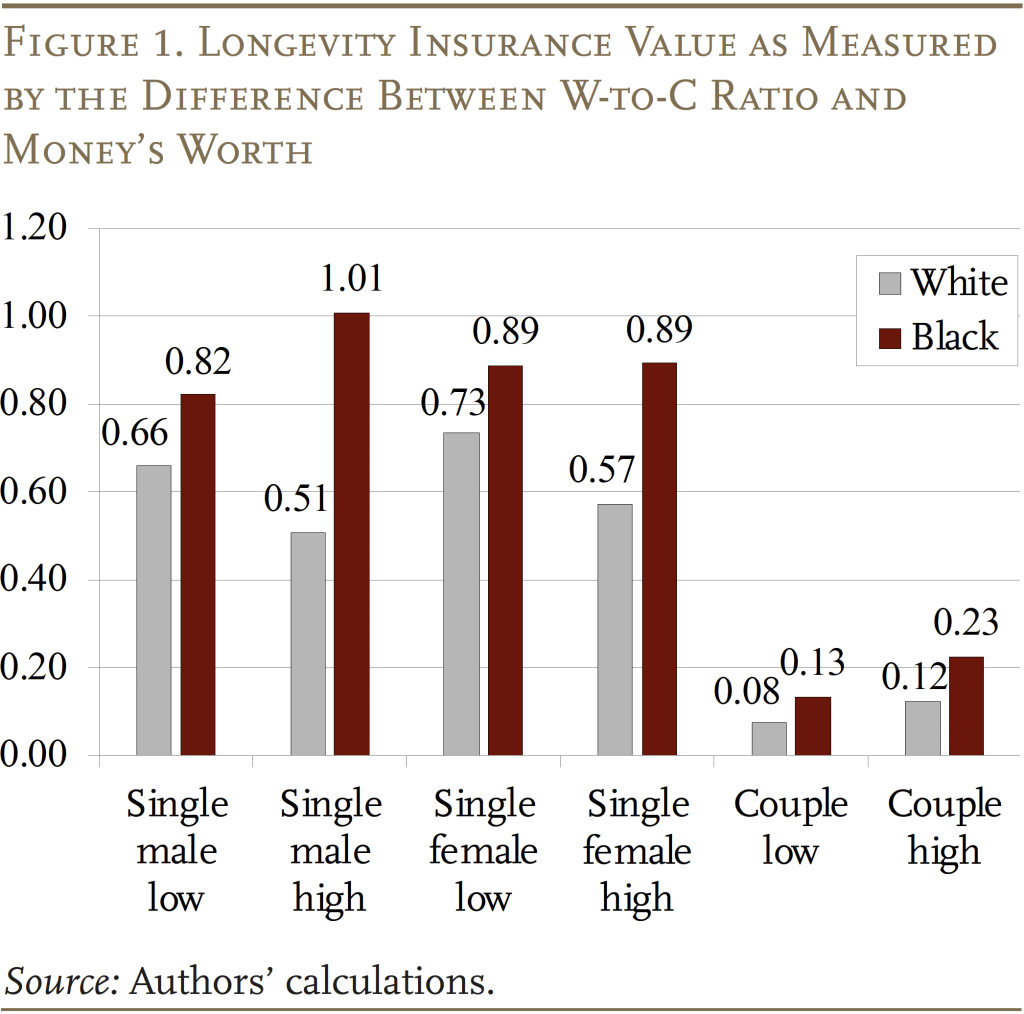
The outcomes additionally present that Black households derive extra insurance coverage worth from OASI than White ones inside every family type-education group, in line with the truth that Black households face higher longevity danger. This outcome means that OASI is an much more necessary consider growing fairness in retirement safety throughout racial teams than is usually recommended by the cash’s value of OASI.
Conclusion
The worth of OASI for various racial and SES teams is usually examined based mostly on this system’s cash’s value, however this method neglects its longevity insurance coverage worth, which is bigger when the dispersion of longevity is bigger. To calculate how the worth of OASI differs throughout racial and SES teams incorporating this system’s longevity insurance coverage worth, this examine calculates the wealth equivalence of OASI advantages utilizing a lifecycle mannequin for stylized households that differ by race, academic attainment, and marital standing.
The outcomes present that the wealth equivalence of OASI is not less than as nice because the lifetime OASI payroll taxes paid for nearly all family varieties, no matter race, gender, schooling, or family composition. This discovering implies households usually want a world by which OASI exists to at least one by which it doesn’t. Evaluating the wealth equivalence with the cash’s value of OASI means that, as soon as insurance coverage worth is accounted for, OASI will increase racial fairness in retirement safety greater than the cash’s value of OASI advantages suggests.
References
Arapakis, Karolos, Gal Wettstein, and Yimeng Yin. 2023. “What Is the Insurance coverage Worth of Social Safety by Race and Socioeconomic Standing?” Working Paper 2023-14. Chestnut Hill, MA: Middle for Retirement Analysis at Boston Faculty.
Clingman, Michael, Kyle Burkhalter, and Chris Chaplain. 2022. “Inside Actual Charges of Return Beneath the OASDI Program for Hypothetical Employees.” Actuarial Word 2021.5. Baltimore, MD: U.S. Social Safety Administration, Workplace of the Chief Actuary.
Kotlikoff, Laurence J. and Avia Spivak. 1981. “The Household as an Incomplete Annuities Market.” Journal of Political Financial system 89(2): 372-391.
Leive, Adam A. and Christopher J. Ruhm. 2021. “Schooling Gradients in Life Expectancy by Gender and Race.” Working Paper 28419. Cambridge, MA: Nationwide Bureau of Financial Analysis.
Sanzenbacher, Geoffrey T. and Jorge D. Ramos-Mercado. 2016. “Calculating Anticipated Social Safety Advantages by Race, Schooling, and Claiming Age.” Working Paper 2016-14. Chestnut Hill, MA: Middle for Retirement Analysis at Boston Faculty.
Sasson, Isaac. 2016. “Developments in Life Expectancy and Lifespan Variation by Instructional Attainment: United States 1990-2010.” Demography 53(2): 269-293.
Wettstein, Gal, Alicia H. Munnell, Wenliang Hou, and Nilufer Gok. 2021. “The Worth of Annuities.” Working Paper 2021-5. Chestnut Hill, MA: Middle for Retirement Analysis at Boston Faculty.

